React Context: Simplifying State Management In the world of React development, managing state efficiently is a crucial aspect of building robust and scalable applications. As your application grows in complexity, passing props down through multiple levels of components can become cumbersome and lead to what's known as "prop drilling." This is where React Context comes in, offering a powerful solution to streamline state management and improve code organization.
However, Apple might not include it in the Air series when it launches it. As for the notebook’s release date, the 15-inch MacBook isn’t coming soon. It’ll get a late 2023 release at best, according to the new claims.
What is React Context?
React Context provides a way to share data (state) between components without explicitly passing props at each level. It essentially creates a "global" data store that any component within a specific tree can access. Think of it like a shared workspace where components can read and sometimes modify data without needing direct connections to every component in between.
More formally:
“
React Context provides a way to share data that can be considered "global" for a tree of React components, without having to pass props down manually at each level.
- Usman


Benefits of Using React Context:
- Eliminates Prop Drilling: The most significant benefit is that it avoids the tedious process of passing props through multiple layers of components. This makes your code cleaner, more readable, and easier to maintain.
- Centralized State Management: Context allows you to manage state in a central location, making it easier to update and track changes. This is particularly useful for data that's used across many parts of your application, like user authentication status, theme settings, or locale preferences.
- Improved Code Organization: By reducing prop drilling, your components become less coupled and more focused on their specific tasks. This leads to better code organization and makes it easier to reason about your application's logic.
- Simplified Updates: When the context value changes, all components that consume that context will automatically re-render. This ensures consistency throughout your application and simplifies the process of updating shared data.
- Easy Access to Shared Data: Components can easily access the context data using the useContext hook (or the older Consumer component). This provides a convenient and efficient way to share data across your component tree.
Where Can You Use React Context?
React Context is ideal for situations where you have data that needs to be accessed by many components, regardless of their position in the component tree. Some common use cases include:
- Themes: Managing the overall theme (light or dark mode) of your application.
- User Authentication: Sharing user authentication status and user data across your app.
- Locale/Language Settings: Providing access to the current language or locale settings.
- Global Configuration: Storing global configuration settings for your application.
- Data Caching: Caching frequently accessed data to improve performance.
- Managing Application-Wide State: For simpler applications, context can be a lightweight way to manage application-wide state. For more complex state management, consider dedicated libraries like Redux or Zustand.
When Not to Use Context:
While Context is a powerful tool, it's not always the best solution. Avoid using Context for data that changes very frequently. The frequent re-renders triggered by context updates can negatively impact performance in such cases. For highly dynamic data, consider other state management solutions or optimize your context usage. Also, for deeply nested component structures where prop drilling is minimal, directly passing props might still be the most straightforward approach.
In the following sections, we'll delve into how to implement React Context and explore its different aspects with practical examples. We'll cover creating a context, providing values, consuming the context, and best practices for using this valuable feature.
Lets explore with example
First we will create new React Project, run below command.
npm create vite@latest my-context-app -- --template react
Once project creation got complete run the following commands
cd my-context-app
npm install
# after installtion
npm run dev
Create new folder contexts
under src, here we can all our required contexts
now create a new file ThemeContexts.jsx in this folder
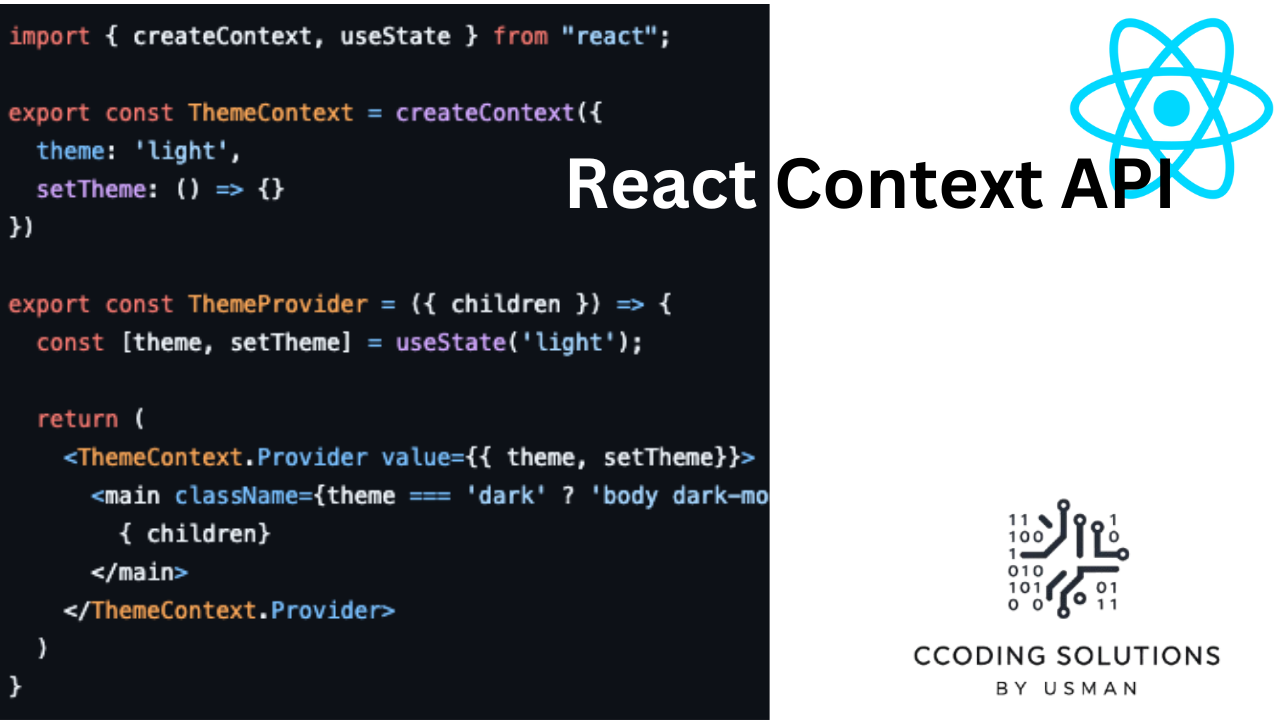
//src/contexts/ThemeContexts.jsx
import { createContext, useState } from "react";
export const ThemeContext = createContext({
theme: 'light',
setTheme: () => {}
})
export const ThemeProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('light');
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{ theme, setTheme}}>
<main className={theme === 'dark' ? 'body dark-mode' : 'body light-mode'}>
{ children}
</main>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
)
}
Hook will help us to access the context anywhere in the app, it will work like an wrapper of this context api
Create new folder hooks
under src, here we can all our required hooks
now create a new file ThemeHooks.jsx in this folder
// src/hooks/ThemeHooks.jsx
import { useContext } from 'react'
import { ThemeContext } from '../contexts/ThemeContexts'
function useTheme() {
const context = useContext(ThemeContext)
return context
}
export default useTheme
Now we are almost there, to test this we need some content so, let's create some component to consume context feature.
create a new folder components and create two files
ExampleComponent.jsx
Navbar.jsx
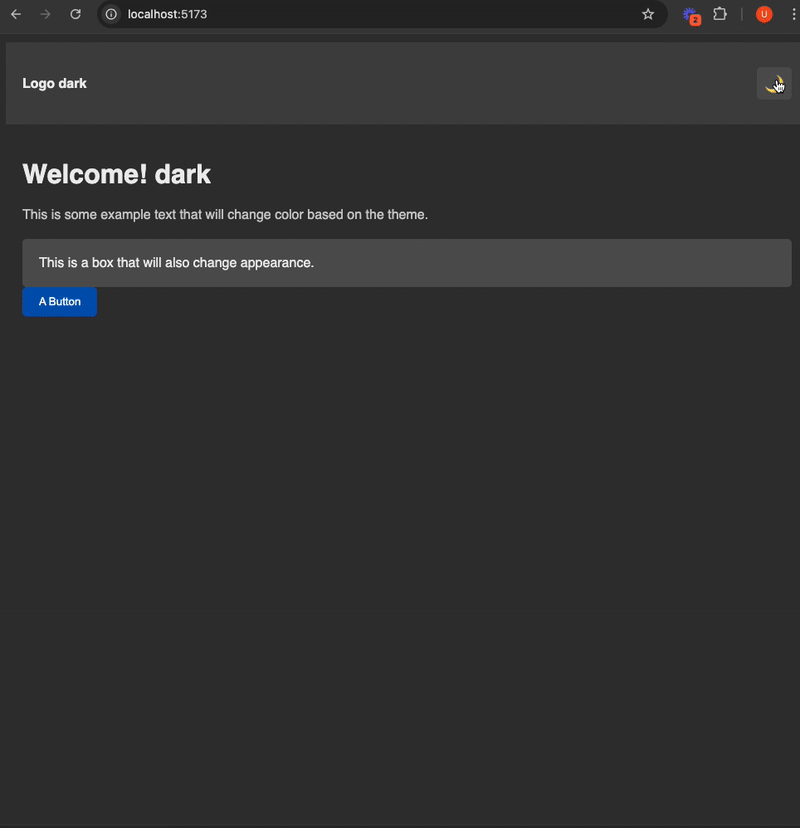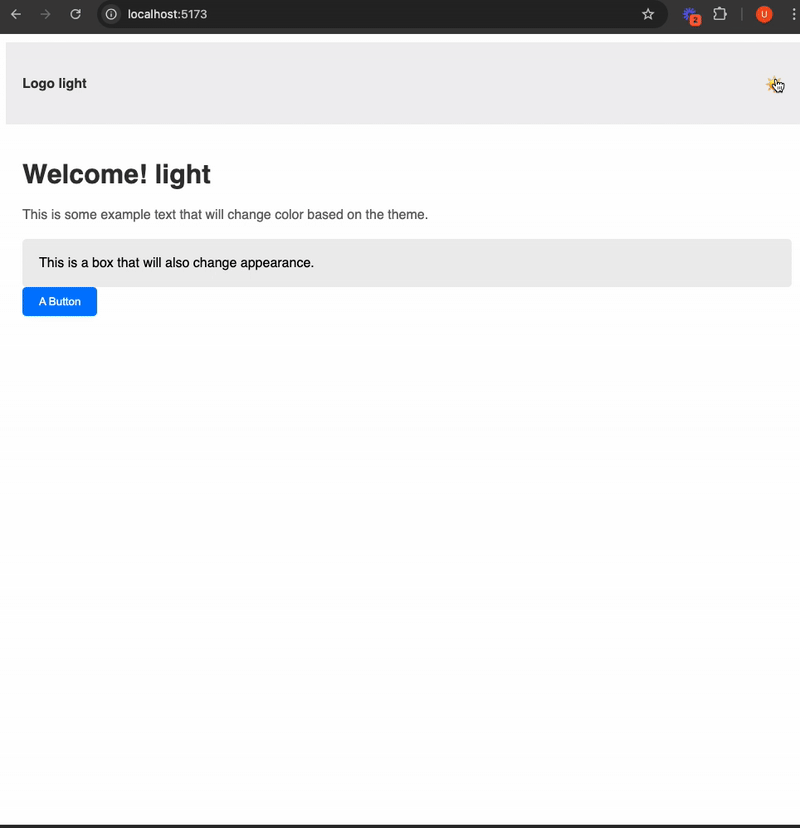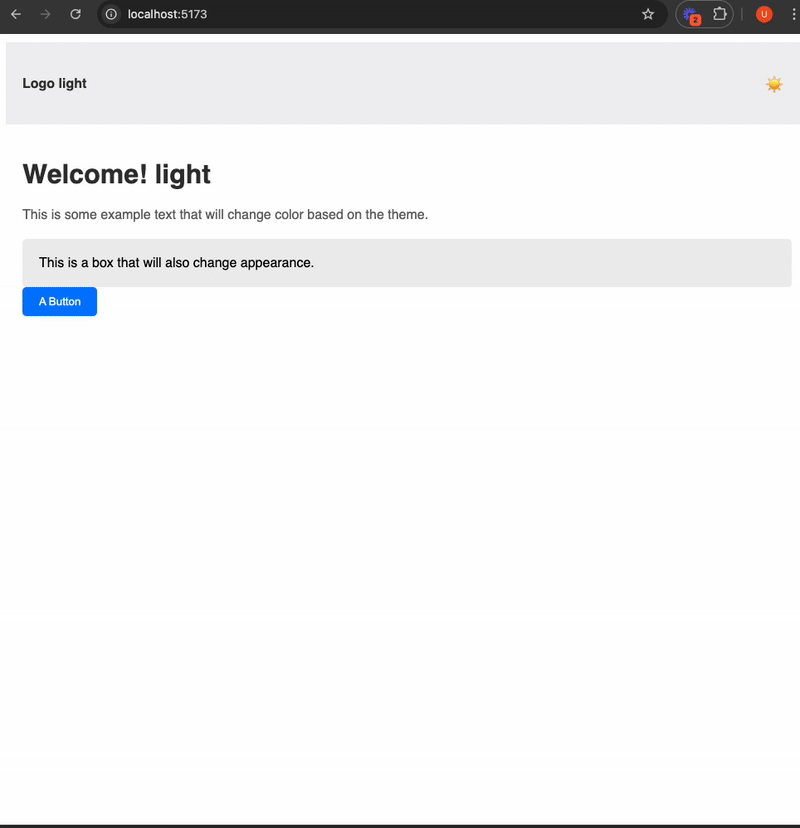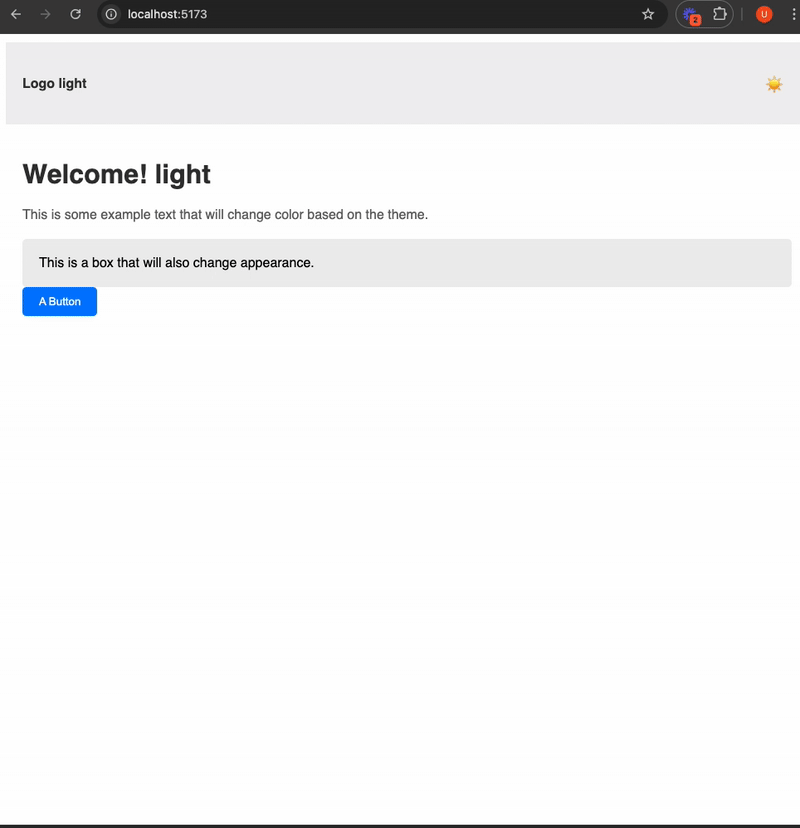
// src/components/ExampleComponent.jsx
import React from 'react'
import useTheme from '../hooks/ThemeHooks'
function ExampleComponent() {
const { theme } = useTheme();
return (
<main className="container">
<h1>Welcome! {theme}</h1>
<p>This is some example text that will change color based on the theme.</p>
<div className="box">
This is a box that will also change appearance.
</div>
<button className="my-button">A Button</button>
</main>
)
}
export default ExampleComponent
// src/components/Navbar.jsx
import useTheme from '../hooks/ThemeHooks'
import React from 'react'
function Navbar() {
const { theme, setTheme } = useTheme();
return (
<nav>
<div className='container'>
<a href="#" className="logo">Logo {theme}</a>
<button id="theme-toggle" onClick={() => setTheme(theme === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light')}>
{theme === 'light' ? (
<span className="light-icon">☀️</span>
) : (
<span className="dark-icon">🌙</span>
)}
</button>
</div>
</nav>
)
}
export default Navbar
Now we only need to add these component in the main component to show. lets add those and update our App.jsx filesrc/App.jsx
// src/App.jsx
import { ThemeProvider } from "./contexts/ThemeContexts"
import Navbar from "./components/Navbar"
import ExampleComponent from "./components/ExampleComponent"
function App() {
return (
<>
<ThemeProvider>
<Navbar />
<ExampleComponent />
</ThemeProvider>
</>
)
}
export default App


No Comments